Juneteenth History
Fort Worth’s contributions to Juneteenth highlight its dual role as a space for acknowledging the past and celebrating progress, while also striving for a more just and equitable future.

Juneteenth History.
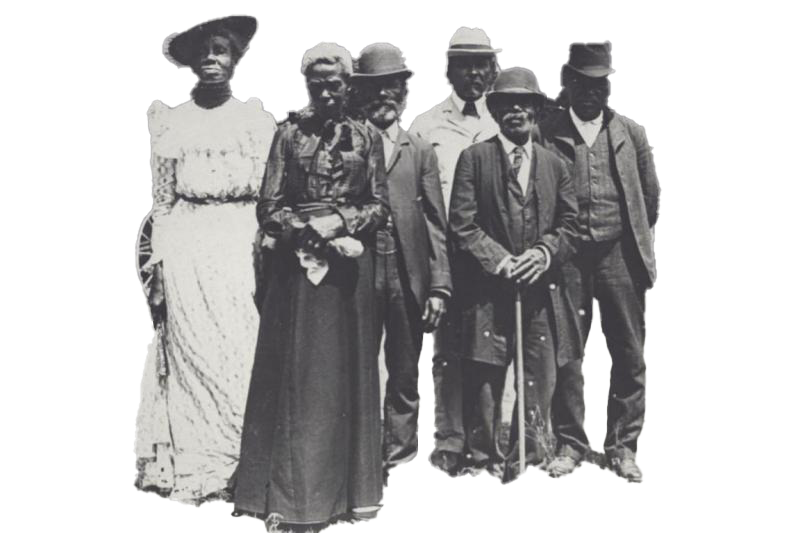
Juneteenth is the oldest internationally celebrated commemoration of the ending of slavery in the United States. Dating back to 1865, it was on June 19th that the Union soldiers, led by Major General Gordon Granger, landed at Galveston, Texas with news that the war had ended and that the enslaved were now free. Note that this was two and a half years after President Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation – which had become official January 1, 1863. The Emancipation Proclamation had little impact on the Texans due to the minimal number of Union troops to enforce the new Executive Order. However, with the surrender of General Lee in April of 1865, and the arrival of General Granger’s regiment, the forces were finally strong enough to influence and overcome the resistance.
Later attempts to explain this two and a half year delay in the receipt of this important news have yielded several versions that have been handed down through the years. Often told is the story of a messenger who was murdered on his way to Texas with the news of freedom. Another is that the news was deliberately withheld by the enslavers to maintain the labor force on the plantations. And still another is that federal troops actually waited for the slave owners to reap the benefits of one last cotton harvest before going to Texas to enforce the Emancipation Proclamation. All of which, or none of these versions could be true. Certainly, for some, President Lincoln’s authority over the rebellious states was in question. Whatever the reasons, conditions in Texas remained status quo well beyond what was statutory.
Opal Lee: Affectionately known as the “Grandmother of Juneteenth,” Opal Lee, a resident of Fort Worth, tirelessly advocated for making Juneteenth a national holiday. Her efforts, including leading 2.5-mile walks symbolizing the delay in Texas learning about emancipation, played a crucial role in its official recognition in 2021.